ethyl cellulose (EC)
Properties and Applications
Ethyl cellulose (EC) is an important commercial cellulose derivative where ethoxy groups have replaced hydroxyl groups on the repeating glucose units. While complete etherification is possible yielding triethyl cellulose, usually only to 2 to 2.5 ethoxyl groups per glucose unit are etherified.
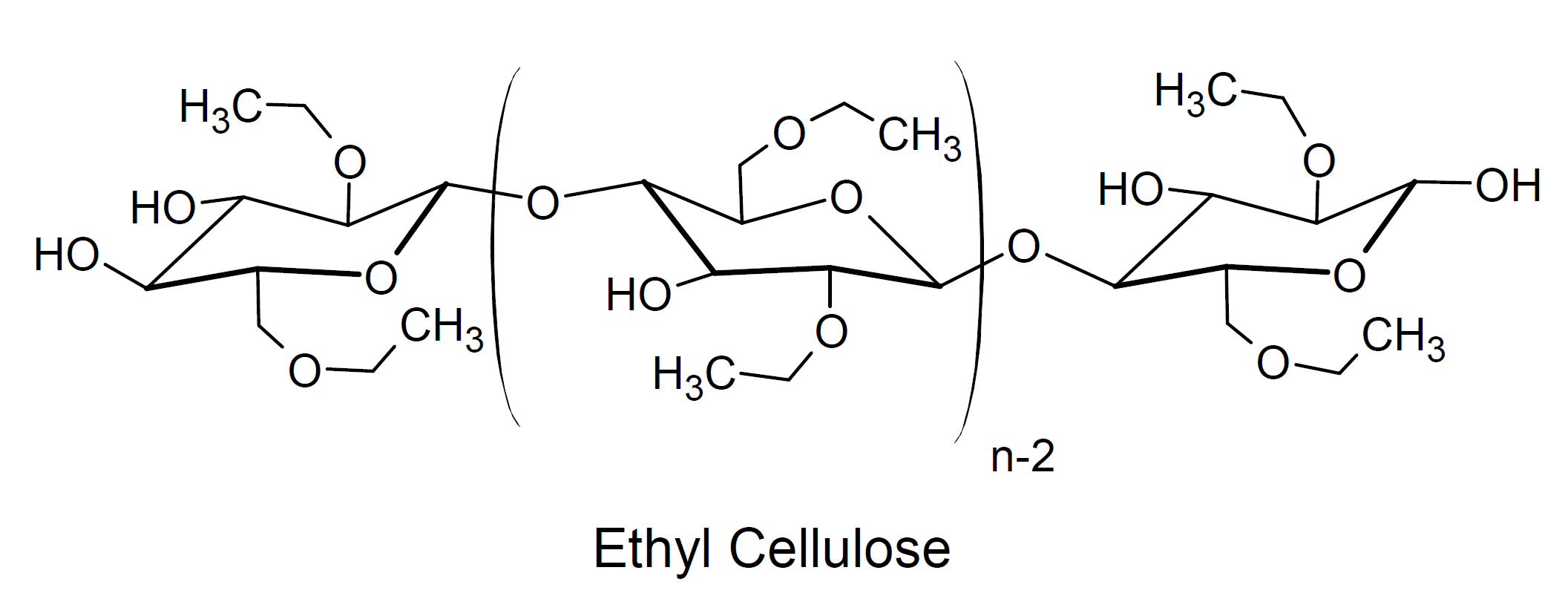
This polymer has excellent strength at room temperature but its strength decreases rapidly with increasing temperature. Like methyl cellulose, it has excellent UV resistance, and is soluble in many organic solvents but not in nonpolar solvents such as aliphatic hydrocarbon oils, natural oils, and greases.
Ethyl cellulose finds uses in food-packaging applications and as a barrier coating for controlled drug release of pharmaceutical products. Heat sealing is difficult unless the surface is activated. Like methyl cellulose (MC), it can also function as a binder, water barrier, rheology modifer, and suspension stabilizer in various other products including printing inks, coatings, textiles, and leather and wood finishes.
Manufacturers & Distributors